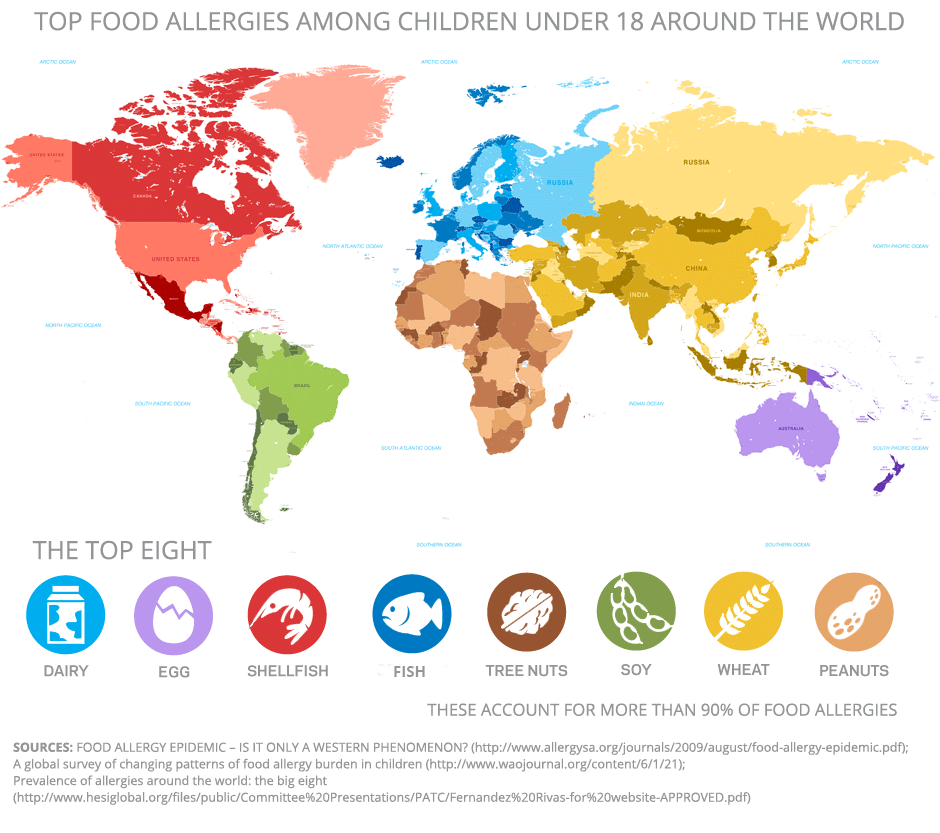
The top 8 allergens are dairy, eggs, nuts, peanuts, soy, shellfish, fish, and wheat, right? Not quite. These 8 foods are the most common food allergens in America, accounting for 90% of food allergies in the US. However, these statistics are slightly different when taking a global perspective. Different countries around the globe have different rates of food allergies to certain foods depending on the local cuisine, gene pool of the region, and environmental factors. As a result, different trends can be observed in different parts of the world:
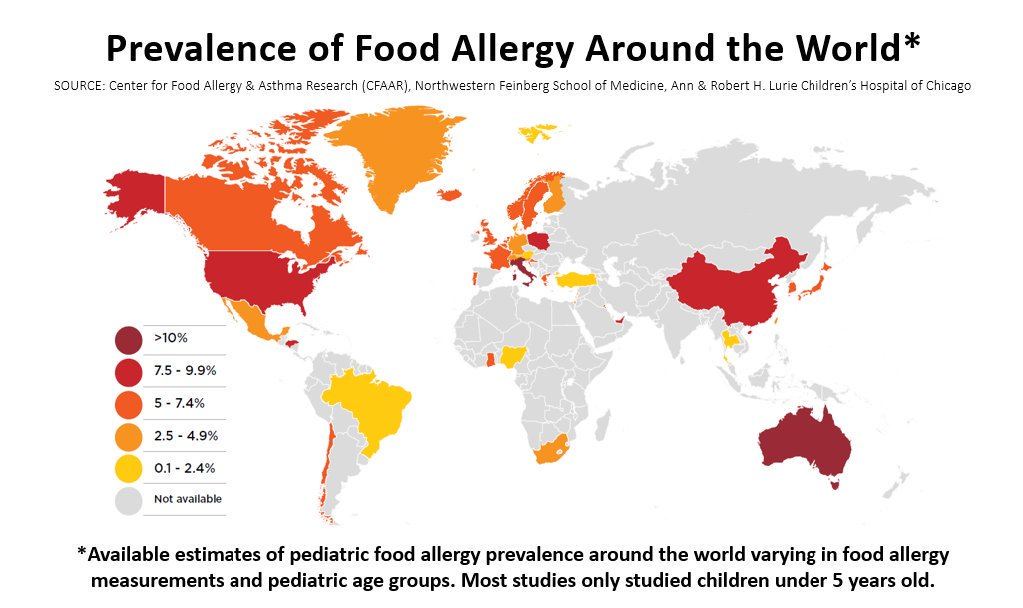
- Countries with the highest rates of food allergies include US, Germany, Italy, and Norway
- Countries with the lowest rates of food allergies include Iceland, Spain, France and the UK
- Children of East Asian or African descent born in the west have higher rates of food allergies than children of Caucasian descent
- Sesame allergies are more prevalent in the Middle East and in parts of Africa than in North America as 43% of anaphylaxis cases in Israeli children are attributed to the seed
Up to 250 million people worldwide have food allergies
http://www.wordallergy.org
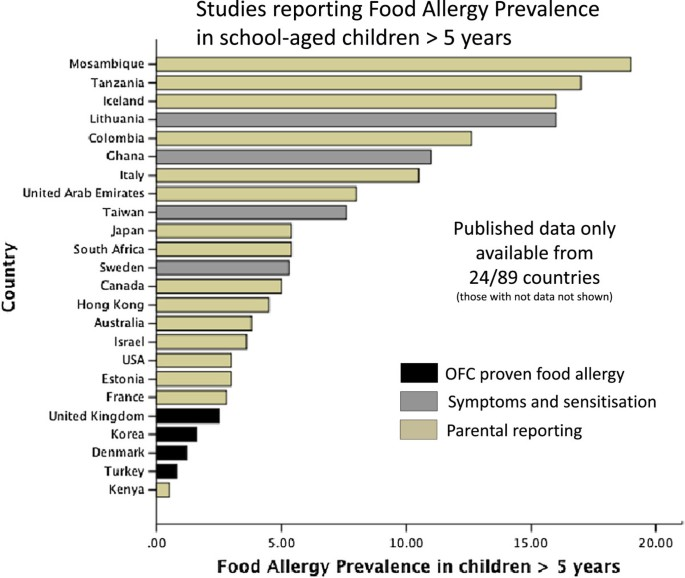
Factors accounting for discrepancies in global patterns of food allergies are varied. While some scientists believe that the prevalence of a specific food in a culture can result in higher rates of allergies to that food, data does not always support this conclusion. For example, sesame allergies are common in the Middle East, which features a sesame heavy cuisine, yet places such as Indonesia and parts of Africa, which have high peanut consumption, actually have lower rates of peanut allergies than average.
Other factors to consider include the healthcare systems of different countries. Many countries rely on self-reported diagnoses in order to collect data, while others group certain allergens such as nuts and sesame or fish and shellfish into a single category, thus skewing data results. Moreover, the gold standard of definitively proving a food allergy diagnosis is a food challenge, but this method can be expensive or unavailable in certain countries.
Finally, globalization and migration means that food allergy trends are always changing. Statistics is a dynamic field, and advances in healthcare, data technology, and communication means that the statistics for food allergies will be changing as well. As immigrants migrate, cultural cuisines will blend, genes will combine in different ways, and new environmental factors may be faced. Thus, global trends in the food allergy field will always be evolving.
Article Sources:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6163515/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6163515/